Coastal cities around the globe are sinking by up to several centimeters per year, on average, satellite observations reveal. The one-two punch of subsiding land and rising seas means that these coastal regions are at greater risk for flooding than previously thought, researchers report in the April 16 Geophysical Research Letters.
Matt Wei, an earth scientist at the University of Rhode Island in Narragansett, and colleagues studied 99 coastal cities on six continents. “We tried to balance population and geographic location,” he says. While subsidence has been measured in cities previously, earlier research has tended to focus on just one city or region. This investigation is different, Wei says. “It’s one of the first to really use data with global coverage.”

Sign Up For the Latest from Science News
Headlines and summaries of the latest Science News articles, delivered to your inbox
Client key* E-mail Address* Go
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
Wei and his team relied on observations made from 2015 to 2020 by a pair of European satellites. Instruments onboard beam microwave signals toward Earth and then record the waves that bounce back. By measuring the timing and intensity of those reflected waves, the team determined the height of the ground with millimeter accuracy. And because each satellite flies over the same part of the planet every 12 days, the researchers were able to trace how the ground deformed over time.
The largest subsidence rates — up to five centimeters per year —are mostly in Asian cities like Tianjin, China; Karachi, Pakistan; and Manila, Philippines, the team found. What’s more, one-third, or 33, of the analyzed cities are sinking in some places by more than a centimeter per year.
That’s a worrying trend, says Darío Solano-Rojas, an earth scientist at the National Autonomous University of Mexico in Mexico City who was not involved in the research. These cities are being hit with a double whammy: At the same time that sea levels are rising due to climate change, the land is sinking (SN: 8/15/18). “Understanding that part of the problem is a big deal,” Solano-Rojas says.
Sinking cities
Satellite measurements of ground height in and around coastal cities, obtained from 2015 to 2020, reveal how fast many are sinking. In parts of some cities, such as these four, the ground is subsiding by more than 10 millimeters per year. Negative values correspond to the ground sinking and moving away from a satellite, while positive ones correspond to the ground rising. The insets show satellite imagery of where subsidence is greatest, indicating that those areas are home to residential or industrial development. The magenta triangles and circles mark Global Navigation Satellite System stations used in the analysis.
Rates at which the ground level is changing in four cities 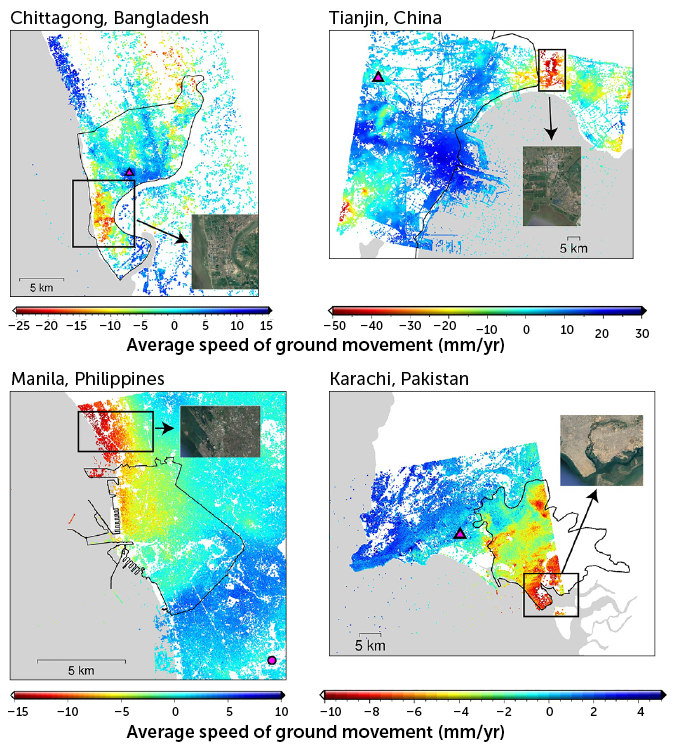 P.-C. Wu, M. Wei and S. D’Hondt/Geophysical Research Letters 2022
P.-C. Wu, M. Wei and S. D’Hondt/Geophysical Research Letters 2022  P.-C. Wu, M. Wei and S. D’Hondt/Geophysical Research Letters 2022
P.-C. Wu, M. Wei and S. D’Hondt/Geophysical Research Letters 2022
Wei and his colleagues think that the subsidence is largely caused by people. When the researchers looked at Google Earth imagery of the regions within cities that were rapidly sinking, the team saw mostly residential or commercial areas. That’s a tip-off that the culprit is groundwater extraction, the team concluded. Landscapes tend to settle as water is pumped out of aquifers (SN: 10/22/12).
But there’s reason to be hopeful. In the past, cities such as Shanghai and Indonesia’s Jakarta were sinking by more than 10 centimeters per year, on average. But now subsidence in those places has slowed, possibly due to recent governmental regulations limiting groundwater extraction.

