Picture a bridge made of Legos. One side has three support pieces, the other two. How would you stabilize the bridge?
Most people would add a piece so that there are three supports on each side, a new study suggests. But why not remove a piece so that each side has two supports instead? It turns out that getting people to subtract — whether a Lego block, ingredients in a recipe or words in an essay — requires reminders and rewards, researchers report April 7 in Nature.
This default to addition isn’t limited to assembling blocks, cooking and writing. Rather, thinking in pluses instead of minuses could well contribute to modern-day excesses such as cluttered homes, institutional red tape and even an overburdened planet, says behavioral scientist Benjamin Converse of the University of Virginia in Charlottesville. “We’re missing an entire class of solutions.”
He and his colleagues first observed the behavior when they asked 1,585 study participants to tackle eight puzzles and problems that could be solved by adding or removing some things. For example, one puzzle required shading or erasing squares on a grid to make a pattern symmetric. In another, individuals could add or subtract items on a travel itinerary for the optimal experience. Across all experiments, the vast majority of participants chose addition over subtraction. For instance, out of 94 participants who completed the grid task, 73 added squares, 18 subtracted squares and another three simply reworked the original number of squares.

Sign Up For the Latest from Science News
Headlines and summaries of the latest Science News articles, delivered to your inbox
Client key* E-mail Address* Go
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
The researchers hypothesized that most participants defaulted to adding because they failed to even think about subtraction. So, through a series of controlled experiments, the team nudged participants toward the minus sign.
In one experiment, the team offered 197 people wandering around a crowded university quad a dollar to solve a puzzle. Participants viewed a Lego structure in which a figurine was standing atop a platform with a large pillar behind her. Atop that pillar, a single block in one corner supported a flat roof. Researchers asked the participants to stabilize the roof to avoid squashing the figurine. About half the participants were told: “Each piece you add costs 10 cents.” Even with that financial penalty, only 40 out of 98 participants thought to remove the destabilizing block and just rest the roof on top of the wide pillar. The researchers gave the remaining participants a more explicit message: “Each piece you add costs 10 cents but removing pieces is free.” That cue prompted 60 out of 99 participants to remove the block.
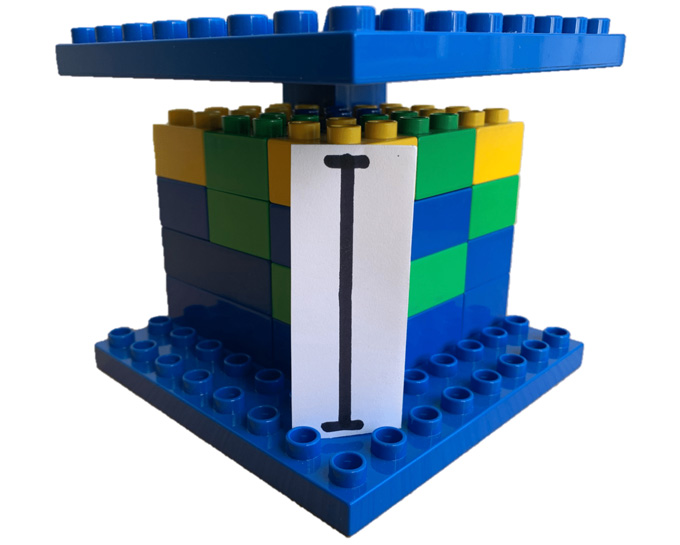 In an experiment, participants had to stabilize a Lego roof over a figurine, represented by the piece of paper. Most people added pieces even though each piece cost 10 cents. Only when researchers specified that subtracting pieces was free did more people remove the destabilizing block and rest the roof on top of the wide pillar.Adams et al/Nature 2021
In an experiment, participants had to stabilize a Lego roof over a figurine, represented by the piece of paper. Most people added pieces even though each piece cost 10 cents. Only when researchers specified that subtracting pieces was free did more people remove the destabilizing block and rest the roof on top of the wide pillar.Adams et al/Nature 2021
Practice did help participants call to mind that elusive minus sign, the researchers found. A variation on the grid experiment, where subtraction yielded the superior solution, showed that three practice runs leading up to the actual task prompted more participants to subtract than those who solved the task without practice.
“When people try to make something better … they don’t think that they can remove or subtract unless they are somehow prompted to do so,” says behavioral scientist Gabrielle Adams, also at the University of Virginia.
Conversely, bombarding participants with unrelated information decreased their likelihood of subtracting (SN: 5/24/20). People add even more when they experience information overload, those experiments showed.
On an intuitive level, people recognize that subtraction comes less naturally than addition, the authors say. Hence the adoption of adages, such as “less is more” and Marie Kondo’s now infamous mantra to get rid of those things that fail to spark joy.
But curbing our love of excess will take more than nudges and a clear mind, says Hal Arkes, a judgement and decision-making researcher at Ohio State University who was not involved with the study. Organizational and political leaders, especially, abhor cutting the fat. “If you add more people and more dollars, you won’t make any enemies, you’ll just make friends,” Arkes says. “Subtraction has serious downsides.”

