Skygazers on the tip of South America were treated Wednesday to a spectacular “ring of fire” solar eclipse that was visible from Chile’s Easter Island before heading to mainland Patagonia.
The rare spectacle—which happens when the sun momentarily all but disappears as the moon crosses its path—drew dozens of tourists, photographers and astronomy enthusiasts to the Pacific island of 7,000 inhabitants.
There, they pointed their lenses at a partly cloudy sky against the backdrop of the “moais”—the giant statues iconic of Easter Island, long inhabited by Polynesian people.
“It was a mini sunset,” 55-year-old Ninoska Huki told AFP of the “sublime” experience that hit the island shortly after noon local time.
A so-called annular solar eclipse occurs when the Earth, moon and sun line up.
Even when perfectly aligned, the moon is too far from Earth to completely block out the sun, creating instead the impression of a fiery ring.
At first, it appears as if a bite has been taken out of the sun.
The bite grows bigger and bigger until the moon moves directly in line with the sun, at which point people nearby usually notice a distinct drop in temperature and brightness but for the ring.
As the day darkens, birds and animals sometimes enter a night-time routine, thinking sunset is near.
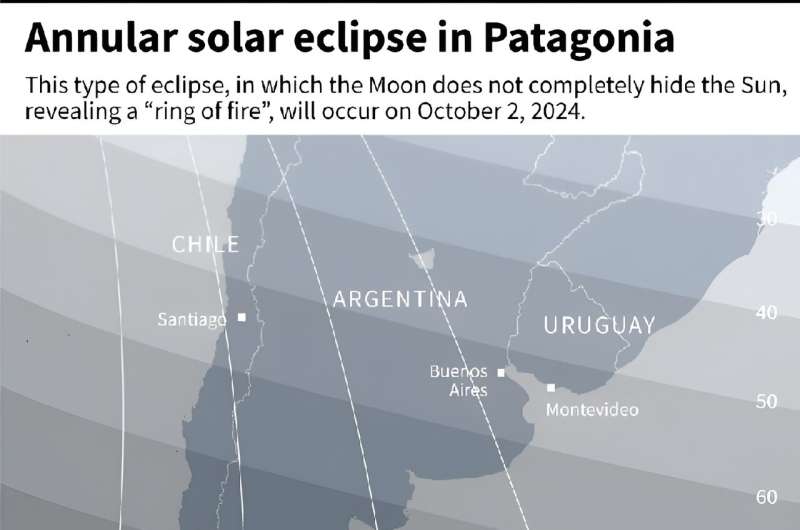
Full “annularity,” the moment of the peak “ring,” lasted about six minutes with Wednesday’s eclipse, which began in the North Pacific before passing over the Andes and Patagonia regions of Latin America.
Lasting more than three hours from about 1700 to 2030 GMT, according to NASA, it was to finish over the Atlantic.
A partial eclipse would be visible from Bolivia, Peru, Paraguay, Uruguay, parts of Brazil, Mexico, New Zealand and several islands in the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, NASA said.
Patagonian path
On the southern tip of Argentina, people braved icy cold and windy weather to gather in the small Patagonian town of Puerto San Julian to observe the phenomenon from an esplanade facing the beach.
Retired teacher Julio Fernandez, 58, brought a telescope “so the children can see, because not many” ever get the chance.
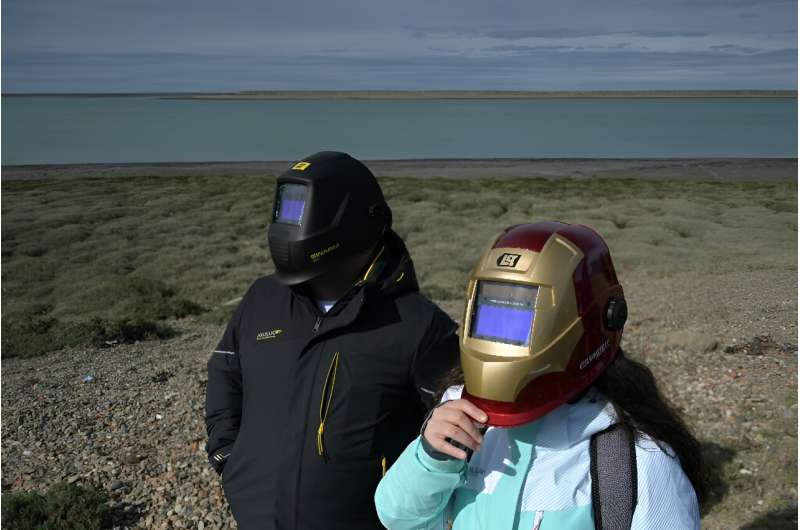

Classes in the town were suspended for children to partake in the rare event.
The only safe methods to observe a “ring of fire” eclipse, according to experts, involve certified special glasses, or watching indirectly through a pinhole in a cardboard sheet projecting the image onto something else.
The next partial solar eclipse will take place on March 29, 2025, visible mainly from western North America, Europe and northwest Africa.
© 2024 AFP
Citation:
South America treated to rare ‘ring of fire’ eclipse (2024, October 3)
retrieved 3 October 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-10-south-america-rare-eclipse.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.

