From creating art and writing code to drafting emails and designing new drugs, generative AI tools are becoming increasingly indispensable for both business and personal use. As demand increases, they will require even more computing power, memory and, therefore, energy. That’s got scientists looking for ways to reduce their energy consumption.
In a paper published in the journal Nature, Aydogan Ozcan, from the University of California Los Angeles, and his colleagues describe the development of an AI image generator that consumes almost no power.
AI image generators use a process called diffusion to generate images from text. First, they are trained on a large dataset of images and repeatedly add a statistical noise, a kind of digital static, until the image has disappeared.
Then, when you give AI a prompt such as “create an image of a house,” it starts with a screen full of static and then reverses the process, gradually removing the noise until the image appears. If you want to perform large-scale tasks, such as creating hundreds of millions of images, this process is slow and energy intensive.
A light-based approach
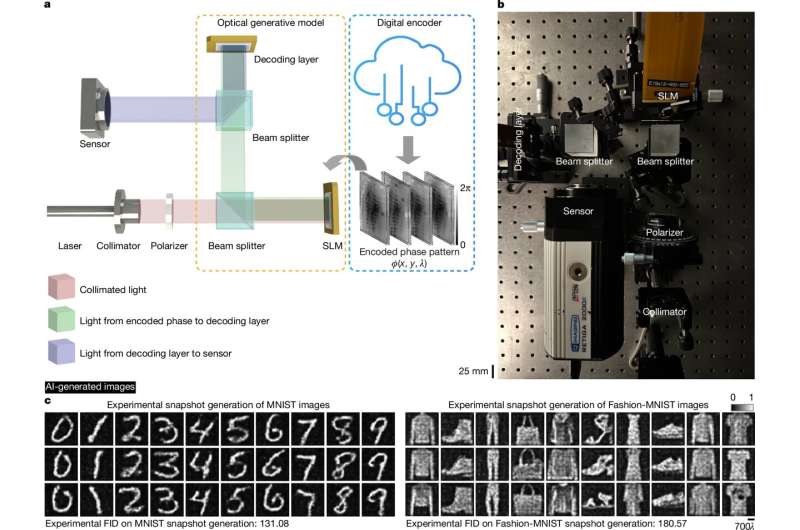
The new diffusion-based image generator works by first using a digital encoder (that has been trained on publicly available datasets) to create the static that will ultimately make the picture. This requires a small amount of energy. Then, a liquid crystal screen known as a spatial light modulator (SLM) imprints this pattern onto a laser beam. The beam is then passed through a second decoding SLM, which turns the pattern in the laser into the final image.
Unlike conventional AI, which relies on millions of computer calculations, this process uses light to do all the heavy lifting. Consequently, the system uses almost no power. “Our optical generative models can synthesize countless images with almost no computing power, offering a scalable and energy-efficient alternative to digital AI models,” said Shiqi Chen, lead author.
The researchers tested their system on various images used to train AI models, including those of celebrities and butterflies, as well as full-color pictures in the style of Dutch painter Vincent Van Gogh.
The results were comparable to those of conventional image generators, but were created with much less energy. This breakthrough has the potential to reduce the carbon footprint of AI-generated content significantly.
The technology could also find its way into a variety of applications. Because the system is so fast and requires minimal energy, it could be used for things like creating images and videos for virtual and augmented reality displays, or for small devices like a smartphone or wearable electronics, such as AI glasses.
Written for you by our author Paul Arnold, edited by Sadie Harley, and fact-checked and reviewed by Robert Egan—this article is the result of careful human work. We rely on readers like you to keep independent science journalism alive.
If this reporting matters to you,
please consider a donation (especially monthly).
You’ll get an ad-free account as a thank-you.
More information:
Shiqi Chen et al, Optical generative models, Nature (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09446-5
Daniel Brunner, Machine-learning model generates images using light, Nature (2025). DOI: 10.1038/d41586-025-02523-9
© 2025 Science X Network
Citation:
The AI breakthrough that uses almost no power to create images (2025, August 28)
retrieved 28 August 2025
from https://techxplore.com/news/2025-08-ai-breakthrough-power-images.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.

