The upcoming XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission, pronounced “crism”) spacecraft will study the universe’s hottest regions, largest structures, and objects with the strongest gravity.
Led by JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), XRISM will peer into these cosmic extremes using spectroscopy, the study of how light and matter interact. In this explainer, video producer Sophia Roberts from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center walks us through how understanding spectroscopy deepens our knowledge of the universe.
“I think we all get excited for the beautiful images we get from missions like NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope,” Roberts said. “But after taking a deep dive into spectroscopy, I really appreciate the critical context it gives scientists about the story behind those pictures.”
XRISM’s microcalorimeter spectrometer, named Resolve, is a collaboration between JAXA and NASA. It will create spectra, measurements of light’s intensity over a range of energies, for X-rays from 400 to 12,000 electron volts. (For comparison, visible light energies range from about 2 to 3 electron volts.)
To do this, Resolve measures tiny temperature changes created when an X-ray hits its 6-by-6-pixel detector. To measure that minuscule increase and determine the X-ray’s energy, the detector needs to cool down to around minus 460° Fahrenheit (around minus 270° Celsius), just a fraction of a degree above absolute zero. The instrument reaches its operating temperature after a multistage mechanical cooling process inside a refrigerator-sized container of liquid helium.
Resolve will help astronomers learn more about the composition and motion of extremely hot gas within clusters of galaxies, near-light-speed particle jets powered by black holes in active galaxies, and other cosmic mysteries.
The Webb telescope captures similar spectra, but for infrared light. Webb’s spectra have revealed the makeup of gas near active black holes and mapped the movement of this material toward or away from the viewer. Data from XRISM’s Resolve instrument will do the same at higher energies, helping paint a fuller picture of these objects.
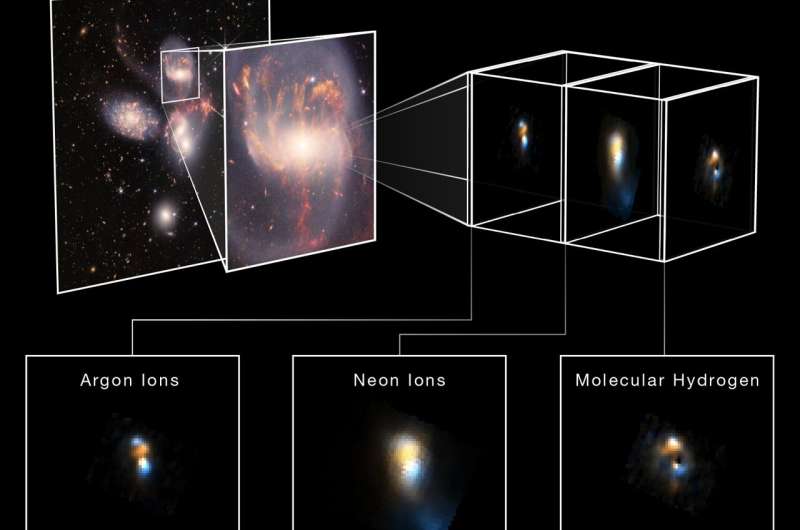
XRISM is a collaborative mission between JAXA and NASA, with participation by ESA (European Space Agency). NASA’s contribution includes science participation from the Canadian Space Agency.
Citation:
XRISM spacecraft will open new window on the X-ray cosmos (2023, August 16)
retrieved 16 August 2023
from https://phys.org/news/2023-08-xrism-spacecraft-window-x-ray-cosmos.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.

