A collaborative team led by researchers from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has successfully developed advanced semiconductor-based radiation detectors, significantly improving their performance for use in extreme environments.
The achievements have been published in a paper in IEEE Electron Device Letters and three articles published in Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A.
Radiation detectors act as the “eyes” for scientists, enabling the observation and study of nuclear radiation and microscopic particles. Traditional detectors, however, often struggle with low sensitivity and limited adaptability to extreme conditions, restricting their effectiveness in high-temperature and high-radiation environments.
In contrast, semiconductor-based detectors made from wide-bandgap and ultra-wide-bandgap materials offer several advantages, including higher temperature resistance, better radiation tolerance, and easier integration, making them promising for advancing radiation detection technology.
The team concentrated on optimizing the design, fabrication processes, and testing methodologies of semiconductor-based radiation detectors to address the shortcomings of existing technologies.
One of the team’s major achievements was the development of large-area detectors made from a combination of p-NiO and β-Ga₂O₃ materials. These materials are known for their low leakage current and enhanced sensitivity. When coupled with specialized neutron detection materials, the team developed a thermal neutron detector made from Ga₂O₃, achieving nearly 1% efficiency in neutron detection—marking a significant milestone as the first successful experimental test of this technology.
-
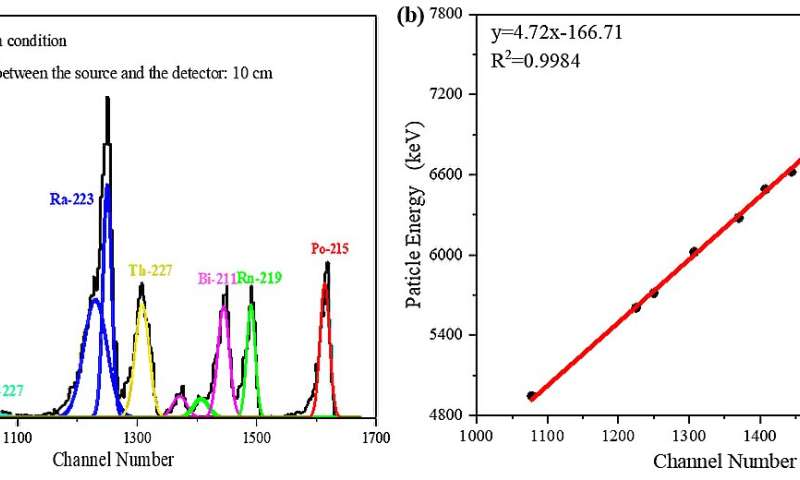
(a) Energy spectrum obtained with a 227Ac source and(b) linear response by 4H-SiC SBD devices. Credit: Han Jingyun
-
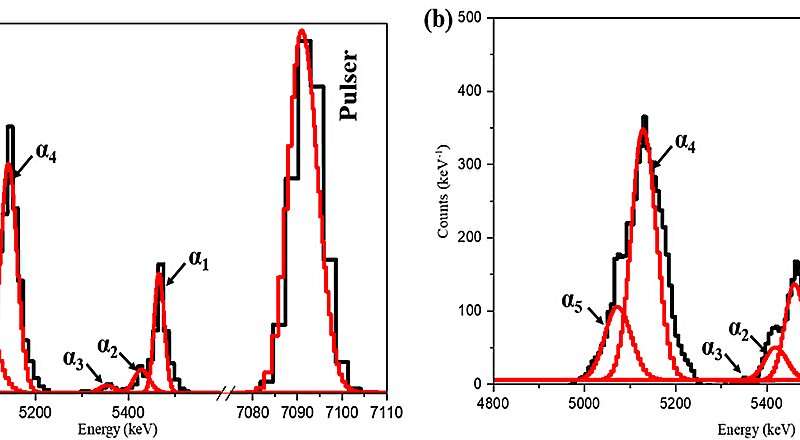
Pulse height spectrum obtained by a 4H-SiC detector with NO annealing aftertreatment progress technique under irradiation of a 239Pu-241Am hybrid source. Credit: Han Jingyun
In another project, the researchers engineered a highly sensitive detector using 4H-SiC, a material capable of withstanding extreme conditions. This detector operates with ultra-low doping levels and thick epitaxial layers, allowing it to accurately measure high-energy particles such as alpha particles. It also demonstrated stable operation at temperatures as high as 80°C for extended periods, which is crucial for studying superheavy elements in demanding environments.
To further improve the detector performance, the researchers developed a specialized annealing process to enhance the interface between the SiC material and its coating. This innovation resulted in an impressive improvement in energy resolution, allowing the detectors to achieve better than 0.5% resolution when detecting alpha particles.
Additionally, the team introduced a new type of thermal neutron detector that employs boron-based materials to boost neutron capture efficiency. This detector can distinguish between two key types of reactions involving thermal neutrons, representing another significant advancement in neutron detection technology.
These innovations signify substantial progress in the development of radiation detectors capable of operating effectively in extreme environments.
More information:
Xiangdong Meng et al, Demonstration of β-Ga2O3-Based Thermal Neutron Detector, IEEE Electron Device Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1109/LED.2024.3522482
Xiang-Dong Meng et al, A novel 4H–SiC thermal neutron detector based on a metal-oxide-semiconductor structure, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.nima.2024.169683
Lei Ren et al, Effect of NO annealing on radiation detection performance of Ni/SiO2/4H-SiC MOS capacitors, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.nima.2024.170073
Lei Ren et al, High performance 4H–SiC detectors for superheavy elements study, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.nima.2024.170181
Citation:
Semiconductor radiation detectors designed for extreme environments (2025, January 17)
retrieved 17 January 2025
from https://techxplore.com/news/2025-01-semiconductor-detectors-extreme-environments.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.

